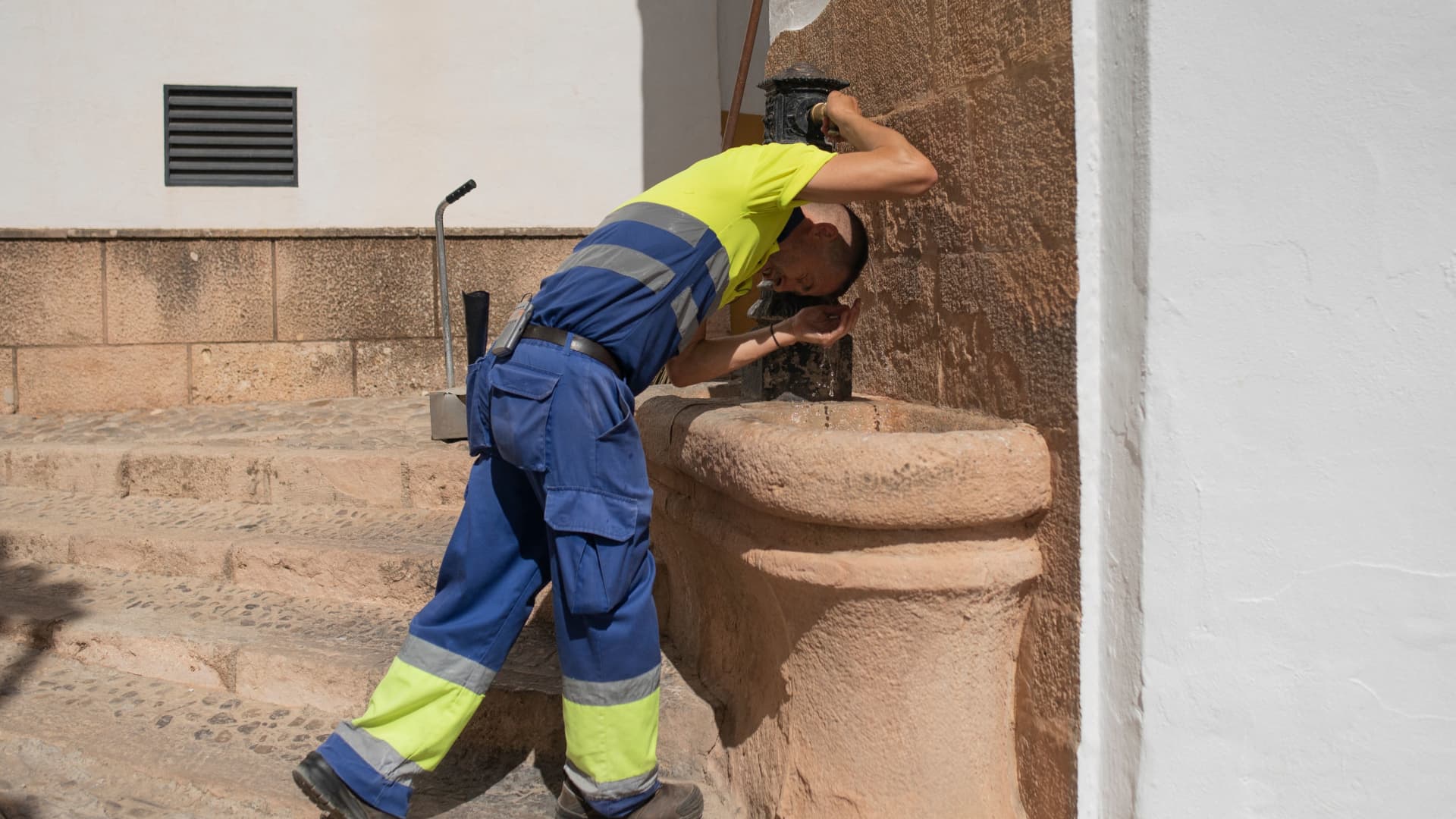
As the world gets hotter, millions of workers face up to the challenge of heat stress and productivity losses
Europe was gripped by punishing heat waves in the summer of 2022, with wildfires, droughts and deaths highlighting what many around the world already know: Weather extremes can have devastating, real-world consequences.
When it comes to temperatures in warmer months, the direction of travel seems to be going one way.
The overall picture is challenging. In May 2023, the World Meteorological Organization said there’s “a 98% likelihood that at least one of the next five years, and the five-year period as a whole, will be the warmest on record.”
The consequences of a warmer planet are going to be multifaceted, affecting billions of people — and the world of work is no exception.
A recent report from the Institution of Mechanical Engineers (IMechE) sketched out how employees could be affected as temperatures rise.
“Thermal comfort is very important in a workplace and if it is not achieved, morale, productivity, health and safety will all likely deteriorate,” the analysis said.
“There’s a whole range of things in addition to just people becoming fatigued and exhausted and not being able to focus on the industrial tasks they’re trying to undertake,” Tim Fox, its lead author.
That includes “increased potential for accidents, because people’s cognitive thinking isn’t as sharp as it would normally be.”
Issues relating to productivity also apply to equipment, facilities and buildings, Fox said. “Overheating ultimately results in economic productivity loss, [it] impacts on national and international economics.” 
Sectors bearing the brunt
Fox and his co-authors are not alone in highlighting the difficulties of a hotter world.
In 2019, the International Labour Organization published a report which contained some sobering details.
“The economic losses due to heat stress at work were estimated at US$280 billion in 1995,” the U.N. agency said.
This, it added, “is projected to increase to US$2,400 billion in 2030, with the impact of heat stress being most pronounced in lower-middle- and low-income countries.”
The ILO’s report also highlighted which sectors would likely bear the brunt of rising average temperatures.
Those working in construction and agriculture, it said, were “expected to be the worst affected, accounting for 60 per cent and 19 per cent, respectively, of working hours lost to heat stress in 2030.”
Heat stress is a serious matter. The ILO describes itas referring to “heat received in excess of that which the body can tolerate without physiological impairment.”
Other outdoor jobs may be affected, too. , Fox highlighted the potential challenges faced by workers in oil refineries, gas plants and chemical works.
All the above roles, he said, involve “quite a lot of external activity,” with workers also needing to wear personal protective equipment, or PPE, thanks to the nature of their job.
“This clothing can be quite cumbersome … and quite hot to wear, even under cold conditions,” Fox said.
That in turn makes employees “particularly at risk or vulnerable to … these sort of conditions.”
Factories are another area of concern. Fox noted that buildings of this type haven’t particularly been designed with heat ingress — especially extreme heat ingress — in mind.
“They’re full of equipment that’s generating a lot of heat, and it’s very difficult for factories, buildings, big warehouse buildings, to passively cool themselves,” he said.
Air conditioning is common in offices, but that’s not the case everywhere, he added.
Fox noted that office buildings in countries with temperate climates, like the U.K., “can get quite hot” because not a lot of air-conditioning had been installed.
Tackling the problem
The overall situation appears grave. For many, preparation and adaptation will be crucial.
The IMechE says this will involve “changes to the design of buildings, infrastructure and other physical assets and systems, both with regard to those that already exist and those that are yet to be built or manufactured, as well as the work, educational, leisure and other activities that humans undertake.”
In a statement issued alongside its report in April, the organization said it also wanted an urgent update to “guidance related to heat impacts on the workforce” so firms can come up with plans and enact changes in their working environments.
At the time, Laura Kent, the IMechE’s public affairs and policy advisor, referenced the challenges authorities face.
“We acknowledge that it would be difficult for the Health and Safety Executive to set a meaningful upper temperature limit due to variations between industries in both working conditions, required PPE and workload,” she said.
“However, HSE guidance needs to be updated to support sectors and industry in the development of appropriate strategies.”
The HSE did not respond request for comment ahead of this story’s publication.
In other parts of the world, plans are being made to ban work when it’s too hot.
In May, for instance, Spain’s Minister of Labour and Social Economy, Yolanda Díaz, tweeted that carrying out “certain jobs during daylight hours” in extreme temperatures would be prohibited.
Speaking to reporters, Díaz said such prohibitions would take effect when AEMET, the State Meteorological Agency, issues red or orange weather alerts.
Citing Spain’s Labour Ministry, Reuters said the move would affect roles in sectors like agriculture and street cleaning. According to Reuters, in the summer of 2022 a street-sweeper in Madrid died from heatstroke.
Trade unions are also making their voice heard when it comes to working in extreme conditions.
Take Unite the Union, which has a presence in Britain and Ireland. It’s listed a range of advice provided by its health and safety representatives to both workers and employers.
Among other things, it stresses the importance of adequate ventilation for internal workspaces, the provision of cover for workers who are in direct sunlight, and stopping all work in extreme conditions.
Among a wide range of actions, Fox stressed the importance of design in creating safe and comfortable working environments in the face of hotter weather.
He said there needs to be a completely new approach to cooling that does not rely on the use of air conditioning, which has a significant environmental footprint.
“We need to explore … more traditional solutions of natural ventilation, use of shade, internal courtyards,” Fox said.
He noted that there’s “an awful lot” that can be done to prepare for the future. Raising awareness would be key. “In many cases, industries and workforces are just not aware that this challenge is coming, and are not preparing for it,” he said.
On top of that, identifying priorities in research and development and updating engineering methodologies and approaches would be needed.
Unless something is done, there will be, “in the coming years and decades, an increase in the economic impact of more extreme heat waves and just the general raising of the ambient seasonal temperature,” Fox warned.
You Might Also Like







