How to make Safe Job Analysis (SJA)
Safe Job Analysis
A safe job analysis is a systematic and stepwise review of all risk factors prior to a given work activity or operation, so that steps can be taken to eliminate or control the identified risk factors during preparation and execution of the work activity or operation.
The term risk factor includes all aspects that directly or indirectly may influence the risk of loss or damage to personnel, the environment or financial assets.
Responsibilities
Operation, Maintenance, Drilling and Well Service, OIM, Group Leaders, Safety Advisors, Process Technicians, Drilling Supervisors and Well Service Supervisors.
2 Abbreviations, definitions and terminology
Abbreviations
| PTW |
Work Permit |
|
SJA |
Safe Job Analysis |
Organization and roles related to SJA
Each installation has its own organizational model with associated functions and work descriptions. Through the use of standard roles in association with SJA, the subject procedure has been made independent of such organizational descriptions.
The procedure does not address the organization of the installations, but it requires that the roles defined in the procedure are taken care of and executed within the individual organizational models.
The following roles have been defined in association with the handling of SJA:
Person responsible for SJA
There must be a person in charge whenever SJA is to be carried out. This may be the person in charge of the execution of the actual work or operation, the area/operations supervisor or someone that is appointed for this role in the particular case. The person responsible for SJA shall make necessary preparations and invite relevant personnel to the SJA meeting. He shall chair the meeting, ensure that the analysis and name of the participants is documented and that responsibility for execution of the identified controls and measures are agreed. Further he shall ensure that a short experience summary is recorded on completion of the actual work or operation. In general, he shall ensure that the SJA is planned and carried out according to the subject document.
Responsible for execution of the work
This is the person responsible for the execution of the actual work.
Executing personnel
Everyone involved in execution of the actual work.
Responsible for measures
The individual persons who are given responsibility for carrying out the identified and documented measures in the SJA.
Area/Operations Supervisor
The management function with operational responsibility over the area or the actual part of the plant or facility that the work will affect, and who therefore will be involved in approval of the work. If the area and operational responsibility is divided between two different positions, both will take part in the performance of this role.
The SJA group
This is the personnel that participate in the SJA. This will normally be all personnel actively involved in the preparation and execution of the work and may include:
-
Person responsible for SJA (must always take part in the SJA meeting)
-
Responsible for execution of the work
-
Area/Operations Supervisor or a person appointed by him/her
-
Area Technician(s)
-
Executing personnel
-
Relevant safety delegates
-
Personnel with specialist knowledge relevant to the analysis
-
HES function
3 Method and requirements when planning and performing SJA
Identify need for SJA
Evaluation of the need for SJA should be done in all phases of the work from the planning stage and all the way through the actual execution. It is a duty of everyone involved in the planning, approval and execution of work activities or work permits to evaluate the need for SJA.
When a need for SJA is identified, a person responsible for SJA must be appointed.
Requirements for use of SJA
General
A safe job analysis is required when risk factors are present or may arise and these factors are not sufficiently identified and controlled through relevant procedures or an approved work permit (WP) associated with the actual work.
This is illustrated in the figure below:
Typical factors to take into account when evaluating the need for SJA:
-
Is the work described in procedures and routines or does it require exceptions from such procedures or routines?
-
Are all risk factors identified and controlled through the work permit?
-
Has this type of work been prone to incidents/accidents?
-
Is the work considered risky, complex or does it involve several disciplines or departments?
-
Are new types of equipment or methods used that are not covered by procedures or routines?
-
Have the personnel involved experience with the actual work or operation?
Method
Operational personnel use the SJA-method to identify and document that the risk factors are under control. If the risk factors are not under control or the potential consequences are very serious, one have to go further and make a more detailed risk analysis.
The performance of a Safe Job Analysis is based on the following stepwise method:
-
Break down the work into basic steps allowing each step and the sequence of the work to be understood by the involved personnel
-
Identify the risk factors and hazards of each step
-
Evaluate the likelihood and severity of the consequences, i.e. the risk in each step
-
Identify measures that eliminate or control the hazards
-
Evaluate and accept the remaining risk
-
Involve the personnel who are part of or influenced by the work in the SJA so that communication and information sharing is facilitated
-
Involve safety delegates and personnel with relevant skills in the analysis
-
Take previous experience into consideration
-
Document the results of the SJA, including identified measures, person responsible for measures and participation in the analysis
-
Review of the SJA when new personnel, who did not participate in the initial SJA, are involved in the work
Planning and performing SJA
Preparing for SJA
The person responsible for SJA will make necessary preparations prior to the SJA meeting. This includes among other activities to:
-
Gather information, drawings, previous experience and any available risk analyses for the actual work
-
Pick up the SJA form and make a preliminary break-down of the work in steps and sequence
-
Evaluate if there are special requirements/preconditions for the work
-
Define the participation in the SJA meeting
-
Call the SJA meeting
The degree and extent of the preparations will depend on the nature of the actual work. For extensive work activities, material will often be prepared well in advance of the actual execution of the work and often by the onshore organisation. A new SJA must be prepared for each individual job (even if a SJA has been performed for a similar type of job at an other point in time), but the use of experience from previous SJA is appropriate and useful to achieve experience transfer.
Performing SJA
The analysis will take place in the SJA meeting
The SJA will be prepared by the SJA group. It is important that all participants get the opportunity to give input and that the analysis is understood by all the involved personnel. Good communication and dialogue in the meeting, ensures that all relevant issues are considered and that the expertise and knowledge of the participants are used to identify the steps of the work, the hazards involved and the arrival at good solutions.
The SJA form in appendix E is to be used for the analysis in the SJA meeting.
Review of the work and preconditions
The person responsible for SJA ensures that the following aspects are reviewed:
-
The actual work to be done
-
The requirements and preconditions to carry out the work
-
Available and relevant preparatory material.
Work site inspection
In most cases it will be necessary to carry out an inspection on the work site as part of the SJA. The SJA meeting will evaluate the need and carry out such an inspection.
Divide the work into basic steps and identify the sequence
Break down the complete task into its basic steps, describing what is to be done. Use words describing actions like “TAKE”, “REMOVE” or “OPEN”.
Identify risk factors and hazards
Identify possible incidents and conditions that can lead to hazardous situations for personnel, the environment or financial assets for each basic task.
Evaluate likelihood and severity
Evaluate for each hazard or risk factor the potential consequences. If the risk factors can give unacceptable consequences, the likelihood is evaluated. The participants have to use their experience and make sound evaluations. (A risk matrix is often used as an aid in this phase of the analysis. An example of such a matrix is given in appendix B.)
Identify measures and controls
Measures and controls that can prevent potential incidents from occurring are preferred instead of measures involving increased emergency response.
Use of the checklist
Use a ”checklist for SJA” as an aid to ensure that potential risk factors, hazards, consequences and measures have been considered. A standard checklist is given in appendix C. This checklist may be supplemented with additional checkpoints or keywords.
Allocate the responsibility for measures
The names of the persons who are responsible for carrying out the identified measures are noted on the SJA form. Those responsible for measures will follow up the work and make sure that the identified measures are carried out.
Evaluate remaining risk and conclude the analysis
Finally the SJA group will make a complete evaluation of the work and draw a conclusion as to whether the work can be carried out or not. It is the opinion of the group that decides whether the remaining risk associated with the work is acceptable.
Document and sign the SJA-form
The SJA is documented in the SJA form and signed by the person responsible for SJA on behalf of the SJA group. The checklist and signed participation list is attached to the SJA form. A standard SJA participant list is provided in appendix D.
Recommendation and approval of the SJA
The SJA-form must be reviewed and recommended by the person responsible for execution of the work and approved by the Area/Operations supervisor. Information about SJA jobs will be given in the daily meeting for coordinating simultaneous activities and work permits on the installation.
Executing the work
Pre-job talk
Unless the SJA meeting was conducted immediately prior to the work, the involved personnel gather to review the work immediately prior to starting the job.
Verify that requirements and preconditions are fulfilled
The person responsible for the work must ensure that requirements and preconditions are satisfied prior to and during the work.
Verify that all measures have been completed
The person responsible for the work must prior to and during the work, ensure that planned measures identified in the SJA are carried out.
Unexpected situations/changes during the course of the work
Should changes arise that are not in accordance with the SJA, the work must be suspended and a new evaluation performed.
Change of personnel
If the responsible for execution of the work leaves the installation, he must appoint a new responsible person for execution and inform involved personnel.
If there are changes of personnel executing the work prior to or during the work, the person responsible for execution of the work will ensure that a detailed review is prepared together with the new personnel. Review of the SJA with new personnel must be documented in the SJA participant list.
Experience transfer, learning and improvement
Evaluate the outcome of the work against the SJA
After completion of the work, the person responsible for SJA will briefly summarize the experiences and record these in the SJA form (Did the requirements/preconditions change? Did unexpected hazards or dangers occur? Did external conditions or interfaces influence the work in ways that were not considered in the SJA?).
Filing SJA-documents
The SJA documentation should be filed according to requirements in the individual operating companies.
Experience transfer, learning and improvement
Experience from work that requires SJA should be used as input when preparing and improving procedures and for future similar work activities according to the requirements in the individual operating companies.
Qualification and training
Platform management must ensure that personnel working on the installation have the necessary knowledge about SJA, in accordance with the role they will have during work activities that require SJA Including SFS interactive e-learning course for SJA.
4 Work process for planning and performing SJA
SJA is planned and carried out according to the main steps in the flow diagram below.
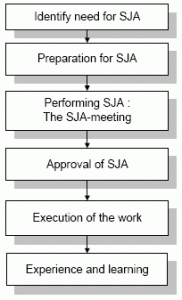
A detailed process flow is shown on the next page.
Appendix A – Guidelines for completion and use of the SJA forms
Introduction
This guideline is written to assist the user in completion and use of the SJA form.
Preparing for SJA
The person responsible for SJA uses the standard SJA form, appendix E and completes the top section:
|
Standard SJA form – top section |
Identification/description of the job and preconditions |
|
SJA Title |
Short title describing the work |
|
SJA No. |
A number identifying the SJA if used by the company |
|
Department/Discipline |
The department or discipline that will carry out the work |
|
Person responsible for SJA |
Name of the person responsible for SJA |
|
Description of the work |
Short description of the work |
|
Installation |
The name of the installation where the work is taking place |
|
Area/Module/Deck |
Name of Area/Module/Deck |
|
Tag. /line no |
Tag or line number of equipment or lines to be worked on |
|
Requirements/Preconditions |
Specify special preconditions for the work, if any |
|
WP/WO No. |
Reference to work permit/work order no. |
|
Number of attachments |
Specify the number of attachments |
It will often be useful that the person responsible for SJA makes a preliminary breakdown of the job in basic steps and fill in the relevant information in the SJA-form.
Performing SJA
The person responsible for SJA chairs the SJA meeting and uses the total expertise of the group to carry out the analysis that is documented in the SJA form (the number of lines in the form may be adjusted according to the actual job):
|
Standard SJA form – middle section |
Breakdown in basic steps, identification of hazards, consequences, measures and responsible for measures |
|
No |
Serial number for that step |
|
Basic steps |
|
|
Hazard/cause |
List the hazards, the causes for potential unwanted incidents that may occur for each step. |
|
Potential consequence |
List potential consequences for each hazard/cause. In this phase a risk matrix like the one in appendix B may be helpful as an aid when doing the risk evaluation. |
|
Measures |
For each consequence when it is considered necessary based on risk, measures are listed. |
|
Person responsible for measures |
The name of the person responsible for each measure is noted. |
At the end of this part of the process, a checklist is used to aid in the assurance that potential hazards and consequences for each step has been considered. The standard checklist for SJA is given in appendix C. Record in the SJA form that the checklist has been used.
On completion of the SJA, the group evaluates whether the remaining risk is acceptable and concludes the analysis. The lower part of the SJA form is used as described below:
|
Standard SJA form – lower section |
Conclusion and approval of the analysis |
|
Is the total risk acceptable (Yes/No)? |
Complete with yes or no |
|
Conclusion/comments |
Fill inn short conclusion of the analysis |
|
Approval: Date/signature |
Fields for signatures |
|
Person responsible for SJA |
Signature by person responsible for SJA on behalf of the SJA group |
Documentation of participation in the SJA is done in the standard SJA participant form, appendix D.
Recommendation and approval of the SJA
|
Standard SJA form – lower section |
Conclusion and approval of the analysis |
|
Approval: Date/signature |
Fields for signatures |
|
Responsible for execution of the work |
Signature for recommendation by person responsible for execution of the work |
|
Area/Operation supervisor |
Approval signature by Area/Operation supervisor |
|
Other position |
Approval signature by other position |
Execution of the work
Prior to start of the work it must be verified that identified measures have been taken care of.
Summary of experience and learning
After completion of the work, the person responsible for SJA will briefly summarise the experiences and record in the relevant section of the SJA form (Did the requirements/preconditions change? Did unexpected hazards or dangers occur? Did external conditions or interfaces influence the work in ways that were not considered in the SJA?).
In this way it will be easy to retrieve and use the experience later or when making improvements to routines and procedures.








